Principle of Inheritance and Variation MCQ/Objective question Chapter 5 Biology Class 12
The study of the organism based on molecular activities like molecular synthesis, interaction, mechanisms, and modifications that occur in a cell and between cell is:
- a. Genetics
- b. Chemology
- c. Molecular biology
- d. Inheritance
Which branch of science deals with the study of genes, the inheritance of characters, and variation?
- a. Endocrinology
- b. Physiology
- c. Genetics
- d. Pharmacology
The term used to assign the process through which charcter pass on from parents to offsprings is:
- a. Genetics
- b. Molecular biology
- c. Inheritance
- d. Variation
Daviation from the parent’s character or trait in a offspring is:
- a. Variation
- b. Inheritance
- c. Genetics
- d. Co dominance
Who proved for the first time that some factors pass on from parents to progeny during sexual reproduction:
- a. Watson and Crick
- b. Khorana
- c. Mendel
- d. Skoog
Law of dominance is:
- a. Expression of one contrasting character over other
- b. Influence of two different characters on each other
- c. Variation in character by the environment
- d. Selection of favourable trait by nature
The genetic character like wrinkled seed/round seed, pod colour, etc are:
- a. Genotype
- b. Phenotype
- c. Both
- d. None
Which among these is not a trait?
- a. Seed color
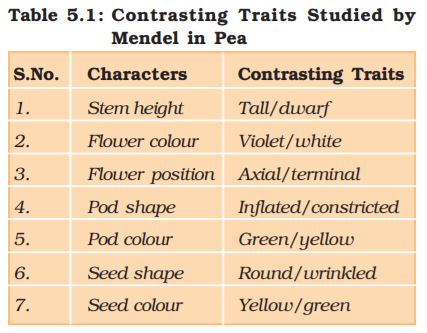
- b. Flower color
- c. Pod shape
- d. Wrinkled seed
The phenotypic ratio that Menndel found during cross pollination of one dominant trait with recessive trait is:
- a.1:1
- b. 2:1
- c. 3:1
- d. 4:1
The resultant genotypic ratio of F1 progeny in Mendel’s experiment is:
- a.1:1
- b. 2:1
- c. 3:1
- d. 4:1
In nature, which character in a pea plant will be more?
- a. Terminal flower
- b. Green Seed
- c. Wrinkled seed
- d. Green pod
Law of dominance works in:
- a. Monohybrid cross
- b. Dihybrid cross
- c. Test cross
- d. All three
When a pure variety of tall pea plant is crossed with a dwarf pea plant, all the progeny is tall. This indicates:
- a. Law of dominance
- b. Law of independent assortment
- c. Co-dominance
- d. Mutiple allelism
Which cross among these is a test cross:
- a. Tt X Tt
- b. Tt X TT
- c. Tt X tt
- d. All
In a test cross F1:
- a. Phenotypic ratio > genotpic ratio
- b. Phenotypic ratio = genotypic ratio
- c. Phenotypic ratio < genotypic ratio
- d. None
Which among these willl show law of independent assortment:
- a.TT X tt
- b. TtRr X ttrr
- c. TTRrYy X TtRrYy
- d. b and c both
The phenotpic ratio in F2 in Mendel’s law of independent assortment is:
- a. 1:1
- b. 3:1
- c. 9:3:3:1
- d. 1:2:1
Law of independent assortment will work for:
- a. Genes on different chromosomes
- b. Linked genes
- c. Character controlled by environment
- d. All
A test cross with pure variety of round seed and green pod will produce:
- a. Round seed with green pod
- b. Wrinkled seed with yellow pod
- c. Half wrinkled half-round seed
- d. Half yellow half green pod
The reason for the un-recognition of Mendel’s law is:
- a. He used mathematics which was new to others.
- b. In nature continuous variation is ubiquitous
- c. That period lacked widespread communication knowledge
- d. All of the above
Chromosomal theory of inheritance was given by:
- a. Hugo De Vries
- b. Sutton and Boveri
- c. Tschmark
- d. Morgan
The traits that Mendel used do not show linkage because:
- a. Linkage show only in sex chromosome
- b. Genes for such trait are located on different chromosomes or are distantly located
- c. Linkage exist only in Drosophila
- d. None
Which among these is not a polygenic inheritance:
- a. Skin color
- b. Turner syndrome
- c. Height
- d. Blood group
Which blood group show co-dominance?
- a. A
- b. B
- c. AB
- d. O
Sex determination in honey bee is by:
- a. XY type
- b. XO type
- c. ZW type
- d. Number of sets of chromosome
Which among these is not a cause of variation in character?
- a. Recombination
- b. Mutation
- c. Environment
- d. None
Which among these is not a autosomal recessive disease?
- a. Sickle cell anemia
- b. Thalassemia
- c. Haemophilia
- d. Phenylketonuria
Assertion:Haemophilc female is rare.
Statement I: Hemophilia is a sex-linked recessive disease
Statement II: Hemophilic male dies early.
- a. Statement I and II both are correct
- b. Statement I and II both are correct and together affirm the cause of assertion.
- c. Only statement I is correct and suffices the assertion
- d. Only Statement II is correct.
Which among these is not a sex-chromosome linked recessive disease?
- a. Colour blindness
- b. Haemophilia
- c. G6PD deficiency
- d. Sickle cell anaemia
Trisomy of chromosome 21 causes:
- a. Down’s syndrome
- b. Klinefelter’s syndrome
- c. Turner syndrome
- d. All three
See also:
Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants MCQ
Principle of Inheritance and Variation MCQ/Objective question Chapter 5 Biology Class 12
Ref: ch5.