Diversity in Living Organisms MCQ/Objective questions Chapter 7 Class 9 Science NCERT
1. Who first tried to classify organisms?
- a. Ernst Haeckel.
- b. Charles Darwin.
- c. Aristotle.
- d. Carolus Linneaus.
2. Binomial nomenclature which we see now was given by?
- a. Ernst Haeckel.
- b. Charles Darwin.
- c. Aristotle.
- d. Carolus Linneaus.
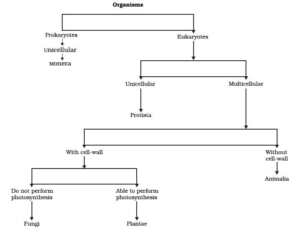
3. A cell with a poorly-defined nucleus is?
- a. Prokaryotic.
- b. Eukaryotic.
- c. Cyanobacteria.
- d. Fungi.
4. A cell with a well-defined nucleus is?
- a. Prokaryotic.
- b. Eukaryotic.
- c. Cyanobacteria.
- d. Fungi.
5. Example of unicellular organisms is/are?
- a. Amoeba.
- b. E.coli.
- c. Paramecium.
- d. All of the above.
6. Photosynthetic organisms is/are?
- a. Plants.
- b. Algae.
- c. Cyanobacteria.
- d. All three.
7. An organism that makes its food from inorganic chemicals are chemoautotrophs. Examples of a chemosynthetic organism are:
- a. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
- b. Sulfur bacteria.
- c. Thermal spring bacteria.
- d. All three.
8. Who wrote the origin of evolution?
- a. Arastu.
- b. Aristotle.
- c. Charles Darwin.
- d. Ernst Haeckel.

- a. Ernst Haeckel.
- b. Robert Whittaker.
- c. Carl Woese.
- d. All three.
Plantae
10. Plants with the poorly-differentiated body that include algae fall into the group?
- a. Thallophyta.
- b. Bryophyta.
- c. Pteridophytes.
- d. All three.
11. Example of thallophytes are:
- a. Spirogyra.
- b. Ulothrix.
- c. Cladophora.
- d. All three.
12. We call _ _ _ _ _ _ Amphibians of a plant kingdom.
- a. Thallophyta.
- b. Bryophyta.
- c. Angiosperms.
- d. All three.
13. Examples of Bryophyta is/are:
- a. Riccia.
- b. Marchantia.
- c. Funaria.
- d. All three.
14. Examples of Pteridophytes is/are:
- a. Marsilea.
- b. Ferns.
- c. Horse-tails.
- d. All three.
15. Pteridophytes are also called Cryptogams. Because they have:
- a. Inconspicuous reproductive organs.
- b. Conspicuous reproductive organs.
- c. None.
16. Phanerogams are plants with conspicuous reproductive organs. They include:
- a. Angiosperms.
- b. Gymnosperms.
- c. Both.
- d. None.
17. Plants with naked seeds are:
- a. Angiosperms.
- b. Gymnosperms.
- c. Both.
- d. None.
18. Plants seeds without ovary include:
- a. Angiosperms.
- b. Gymnosperms.
- c. Both.
- d. None.
19. Which among these are ornamental plants:
- a. Angiosperms.
- b. Gymnosperms.
- c. Both.
- d. None.
20. Which among these are flowering plants:
- a. Angiosperms.
- b. Gymnosperms.
- c. Both.
- d. None.
21. Plants seeds inside the ovary include:
- a. Angiosperms.
- b. Gymnosperms.
- c. Both.
- d. None.
22. Angispermic plants seeds with one cotyledon are:
- a. Monocot.
- b. Dicot.
- c. Both.
- d. None.
23. Angispermic plants seeds with two cotyledons are:
- a. Monocot.
- b. Dicot.
- c. Both.
- d. None.
24. Which is the most advanced plants :
- a. Monocot.
- b. Dicot.
- c. Pteridophytes.
- d. Bryophytes.
25. Plants in the given picture belong to the group :
- a. Monocot.
- b. Dicot.
- c. Pteridophytes.
- d. Bryophytes.
Animalia
26. The simplest animal is :
- a. Porifera.
- b. Cnidaria.
- c. Platyhelminthes.
- d. Nemetehelminthes.
27. Coelenterata has:
- a. True coelom.
- b. False coelom.
- c. no coelom.
- d. None.
28. We see the primitive type of tissue differentiation in animals in:
- a. Porifera.
- b. Cnidaria.
- c. Platyhelminthes.
- d. Nemetehelminthes.
29. Platyhelminthes are:
- a. Monoblastic.
- b. Diploblastic.
- c. Triploblastic.
- d. None.
- a. Planaria.
- b. Liver fluke.
- c. Tapeworm.
- d. All.
31. Which among these have a triploblastic symmetrical body:
- a. Platyhelminthes.
- b. Nemetehelminthes.
- c. Nematodes.
- d. Annelids.
32. We see true coelom in earthworm and leeches. They belong to:
- a. Platyhelminthes.
- b. Nemetehelminthes.
- c. Nematodes.
- d. Annelids.
33. Arthropods are the _ _ _ _ _ groups of animals.
a. Biggest.
c. Smallest.
34. We see an open circulatory system in:
- a. Nemetehelminthes.
- b. Nematodes.
- c. Annelids.
- d. Arthropods
35. Arthropods means:
- a. Bent legs.
- b. Jointed legs.
- c. False legs.
- d. True legs.
36. Spinny skinned animals belong to the group:
- a. Echinodermata.
- b. Protochordate.
- c. Mollusks.
- d. None.
Explanation:
1. Aristotle first classified organisms into aquatic and land animals.
9. All three worked together and classified organisms into broad categories called Kingdom.
See also:
Answer:
| 1. a | 10. a | 19.b | 28. c |
| 2. d | 11. d | 20. a | 29. b |
| 3. a | 12. b | 21. a | 30. d |
| 4. b | 13. d | 22. a | 31.b |
| 5. d | 14. d | 23. b | 32,d |
| 6. d | 15.a | 24. a | 33.a |
| 7. d | 16. c | 25. c | 34.d |
| 8. c | 17. b | 26. a | 35. b |
| 9. b | 18. b | 27. b | 36.a |
Diversity in Living Organisms MCQ/Objective questions Chapter 7 Class 9 Science NCERT
Ref: Chapter 7, NCERT.