Morphology of Flowering plants MCQ/Objective questions Biology Class 11 Chapter 5
1. Radicle in most dicots form _ _ _ _ _ while plumule forms _ _ _ _ _.
- a. Primary root, Stem.
- b. Stem, leaves.
- c. Leaves, stem.
- d. Stem, Primary root.
2. We can see the short-lived primary root in:
- a. Gymnosperms.
- b. Dicots.
- c. Monocots.
- d. None.
3. Adventitious root may arise from
- a. Rhizome.
- b. Leave.
- c. Stem
- d. Any of the above.
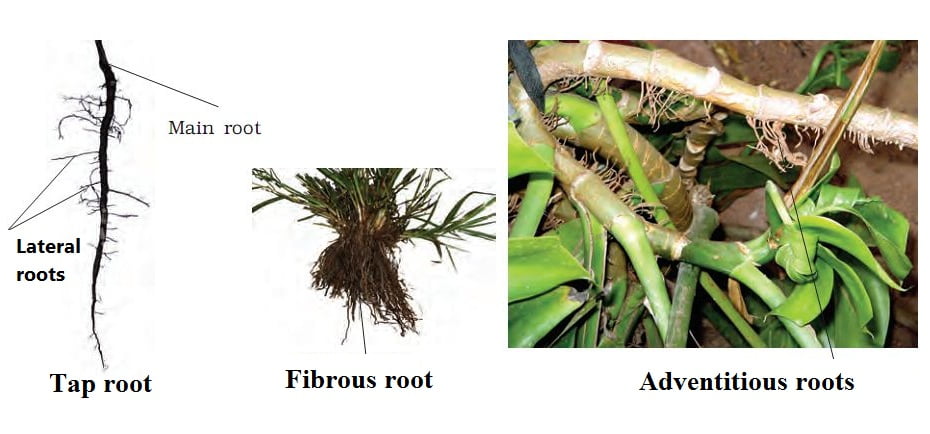

- a. Taproot system.
- b. Fibrous root system.
- c. Adventitious roots.
- d. None.
5. Following part of the root divides actively (has meristem tissue):
- a. Root cap.
- b. Root hairs.
- c. A few millimeter above root cap.
- d. None.
6. Following plants have modified root which store food:
- a. Onion.
- b. Turnip.
- c. Sweet potato.
- d. All above.
7. Extra roots of the banyan tree that provide additional support to the tree is c/a:
- a. Taproot system.
- b. Fibrous root system.
- c. Prop roots.
- d. None.
8. Pneumetaphoric roots of swamp plant move upward to provide:
- a. Food from the air.
- b. Water from humidity.
- c. Oxygen from the atmosphere.
- d. None.
9. Modification of stem is/are:
- a. Tendril.
- b. Thorn.
- c. Rhizome.
- d. All of the above.
10. Leaves born from:
- a. Nodes.
- b. Internodes.
- c. Both
- d. None.
11. Parts of a typical leaf consist of:
1. Leaf blade, 2. Petole, 3. Lamina.
- a. 1 and 2.
- b. 2 and 3.
- c. 1 and 3.
- d. 1, 2 and 3 all.
- a. Reticulate.
- b. Parallel.
- c. Complex.
- d. None.
13. Venation in most monocot is:
- a. Reticulate.
- b. Parallel.
- c. Complex.
- d. None.
.
- a. Simple leaf.
- b. Compound leaf.
- c. Mixed leaf.
- d. Complex leaf.
15. Alternate, opposite, and whorl leaves contain X number of leaves at the node respectively.
- a. 1, 2, 3.
- b. 3, 2, 1.
- c. 1, 2, and more than two.
- d. None.
16. What is inflorescence?
- a. Arrangement of leaflets on a stem axis.
- b. Arrangement of florets on a floral axix.
- c. Arrangement of flowers on a floral axis.
- d. None
- a. Terminate into flower.
- b. Grows continuously and flowers appear laterally
- c. Convert into flower.
- d. None.
18. In cymose inflorescence, floral axis:
- a. Terminate into flower.
- b. Grows continuously and flowers appear laterally
- c. Convert into flower.
- d. None.
- a. Superior.
- b. Inferior.
- c. Complex.
- d. None.
Next:
- The Living world MCQ Biology Questions
- Biological Classification MCQ Questions with answers
- Plant Kingdom MCQ Biology Class Eleven
- Animal Kingdom MCQ Biology
- Morphology of Flowering Plants MCQ
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants MCQ Biology
- Structural Organisation in Animals MCQ
Animal Kingdom MCQ/Objective questions Chapter 4 Biology Class 11
Ref: Chapter 5, NCERT.