Human Reproduction MCQ/Objective questions Chapter 3 Class 12 Biology
Which among these is not a typical reproductive event in human life?
- a. Formation of gametes
- b. The fusion of gametes
- c. Development of a fetus
- d. Abortion
Table of Contents
The Male Reproductive system
Strike out the one which is not related with man reproductive system:
- a. Testes
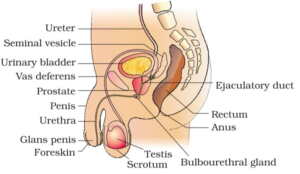
- b. Ejaculatory duct
- c. Penis
- d. Fallopian tube
The pouch outside the abdominal cavity that keep testes is:
- a. Urinary bladder
- b. Scrotum
- c. vas defrens
- d. Seminal vesicle
Which part of testis produces testosterone hormone?
- a. Interstitial cells of Leydig
- b. Seminiferous tubule
- c. Sertoli cells
- d. Rete testis
The cells that provide nutrient to germ cells inside seminiferous tubules is:
- a. Leydig cell
- b. Sertoli cells
- c. Spermatogonia
- d. None
Produced sperms inside the testis are stored for weeks and matures in:
- a. Rete testis
- b. Epididymis
- c. Vas defrens
- d. Vasa efferentia
Why blood do not supply nutrition directly to germ cells?
- a. Blood capillaries will increase the temperature of the testis
- b. WBC’s of blood will destroy the gametes as the later is haploid
- c. Blood does not contain the nutrient specific to growing sperm
- d. None
Vas deferens receives ducts from the seminal vesicle and open into:
- a. Rete testis
- b. Ejaculatory duct
- c. Epididymis
- d. Urinary tract
The male accessory gland whose secretion llubricate the penis is:
- a. Seminal vesicle
- b. Prostate
- c. Bulbourethral gland
- d. None
The Female Reproductive System
Which among these is not a part of female reproductive system?
- a. Uterus
- b. Cervix
- c. Mammary gland
- d. Prostate
Which female sex organ is not a paired structure?
- a. Ovary
- b. Fallopian tube
- c. Uterus
- d. All three
Implantation of the embryo occurs in
- a. Ovary
- b. Fallopian tube
- c. Uterus
- d. Cervix
The female hormone that produces milk in mammary glands is:
- a. Oxtotocin
- b. Prolactin
- c. Vasopressin
- d. FSh
Gametogenesis
How many spermatids are formed from one primary spermatocytes?
- a. One
- b. Two
- c. Three
- d. Four
The hormone that control the function of testis is:
- a. GnRH
- b. LH
- c. FSH
- d. All three
The enzyme filled sac that help sperm penetrate the ovum is:
- a. Acrosome
- b. Neck
- c. Middle piece
- d. Tail
The number of ovum formed by one primary oocyte is:
- a. One
- b. Two
- c. Three
- d. Four
At birth all the female germ cell is at
- a. Oogonia
- b. Primary oocyte
- c. Secondary oocyte
- d. Ovum
How many days are there in a typical menstrual cycle?
- a. 14
- b. 28
- c. 32
- d. 62
On which day of menstrual cycle ovulation occurs?
- a. 14
- b. 28
- c. 32
- d. 62
Hormone that lead to ovulation is:
- a. LH
- b. Estrogen
- c. Progesterone
- d. None
The hormone responsible for consistency and growth of endometrium is:
- a. LH
- b. Estrogen
- c. Progesterone
- d. None
The part of ovary that degenerates in the absence of fertilization and produce progesterone is:
- a. Endometrium
- b. Primary follicle
- c. Graffian follicle
- d. Corpus luteum
Fertilization
Fertilaztion occurs in:
- a. Ovary
- b. Fallopian tube
- c. Uterus
- d. Cervix
The enzyme filled sac that help sperm penetrate the ovum is:
- a. Acrosome
- b. Neck
- c. Middle piece
- d. Tail
When meiosis 2 of secondary oocyte occurs?
- a. At birth
- b. At puberty
- c. Once sperm enter the cytoplasm of the oocyte
- d. At birth
Implantation occurs on which day after fertilization?
- a. one
- b. 2-3days
- c. 5-6days
- d. 16days
How many cells are there in a developing morula ?
- a. 8
- b. 16
- c. 32
- d. 128
Which among these is not a placental hormone?
- a. hCG, hPL
- b. Estrogen, progestron
- c. Relaxin
- d. FSH
Hormone that increase uterine contraction during parturition is
- a. Prolactin
- b. Oxytocin
- c. Vasopressin
- d. Estrogen
The milk produced for a few days after birth is rich in nutrients and antibodies. This milk is called
- a. menarche
- b. Colostrum
- c. Oogenesis
- d. Fetus
See also:
Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants MCQ
Human Reproduction MCQ/Objective questions Chapter 3 Class 12 Biology
ref: ch3.