The Fundamental Unit of Life MCQ – Objective Questions with answers
1. The English scientist who first observed a cell and coined the term ‘cell” was…
2. which object did he use to observe cells?
a. Onion bulb b. Potato c. Cork d. None.
3. ‘Cell’ is a Latin word which means…
a. a large room b. a little room c. An old room d. None.
4. Few examples of a unicellular organism are…
5. A human cell consists of…
(name some inner organelles of the cell)
6. Plant cell contains…
a. Chlorophyll b. Cell wall c. Nucleus d. Plastid e. All.
7. A cell wall is present only in…
a. Plant cells b. Bacterial cells c. Animal cells d. a and b
8. A plasma membrane is a selectively-permeable membrane while a cell wall is…
a. Semi-permeable b. fully-permeable c. Selectively permeable d. Non-permeable.
9. Carbon dioxide moves out of the cell by the process…
a. Osmosis b. Actively c. Diffusion.
10. Water move in and out of the cell by the process…
a. Osmosis b. Actively c. Diffusion.
11. In a saline solution, a cell will:
a. Swell b. Shrink c. Burst.
12. In distilled water, a cell will…
a. Swell b. Shrink c. Burst.
13. An egg is a ….. celled structure.
a. Multi-cellelular b. Single-celled.
14. A plasma membrane consists of:
a. Chitin b. Cellulose c. Protein and lipid. d. Fibre.
15. Amoeba acquires his food by the process…
a. Exocytocis b. Ingestion c. Endocytosis
Table of Contents
The Fundamental Unit of Life MCQ
16. A plant cell wall is mainly composed of …
a. Lipd b. Cellulose c. Fibre. d. Chitin.
17. ….. is the shrinkage of a cell in water.
a. Plasmolysis b. Karyokinesis c. Meiosis.
18. Genetic material inside a cell is confined to …
- a. Between cell wall and cell membrane.
- b. Nucleus.
- c. Cytoplasm.
12. Examples of double-membraned organelles are…
a. Nucleus b. Mitochondria c. Plastid d. All
13. A cell with a well-defined nucleus is…
a. Prokaryote b. Eukaryote.
14. A cell with a poorly defined nucleus is…
a. Prokaryote b. Eukaryote.
15. Animals, plants, and amoeba are prokaryote or eukaryote?
a. Prokaryote b. Eukaryote.
16. Examples of prokaryotes are…
a. Bacteria b. Fungi c. Virus d. Plants.
17. Protoplasm = Cell – (Cell wall + ……)
a. Plasma mebrane b. Cytoplasm c. Organelles d. Plastids.
18. Cytoplasm = Protoplasm – ……
a. Plasma mebrane b. Cytoplasm c. Organelles d. Nucleus.
19. Organelles in eukaryotic cells are membrane-bound or without membrane.
20. Organelles in a ……. cell are not membrane-bound
a. Prokaryotic cell b. Virus c. Animal d. a and b.
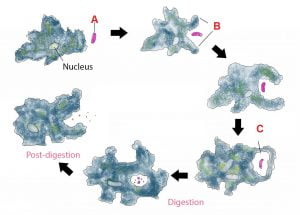
21. Identify the marked subjects in the image.
22. The above process of food intake by amoeba is…
23. The network of the tube-like structure in a cell is…
a. Golgi body b. Endoplasmic reticulum c. Mitochondria d. Chloroplast.
24. We say Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum as rough because ……. are attached to it.
a. smooth endoplasmic reticulum b. Mitochindria c. Ribosome d. Nucleus.
25. SER stands for…
24. RER does protein synthesis while SER does…
a. ATP b. Lipid c. Catbohydrate d. ADP.
25. Other functions of the endoplasmic reticulum are:
a. Protein transport (RER) b. Detoxification in liver cells (SER) c. Glucose synthesis d. a and b.
26. Membrane-bound flattened sacs (vesicles) arranged parallelly in a cell are…
a. ER b. Nucleus c. Lysosome d. Golgi body.
27. Storing, packaging, and modification of newly formed protein occur in:
a. ER b. Nucleus c. Lysosome d. Golgi body.
28. With the help of enzymes from RER, Golgi bodies also form…
a. Vacuoles b. Lysosomes c. Mitochondria d. None.
29. Lysosomes are membrane-bound sacs filled with
a. Toxic wastes b. Digestive enzymes c. Immune cells d. Glucose.
30. Suicidal bags of cells are…
a. Vacuoles b. Lysosomes c. Mitochondria d. None.
Class 9 Science Chapter 5 MCQ
31. Lysosomes help in the ……. of the food.
a. Ingestion b. Digestion c. Elimination d. None
32. The powerhouse of a cell is:
a. Mitochondria b. Plastid c. Nucleus d. Glucose.
33. Which part of the mitochondrial membrane form ATP?
a. Outer membrane b. Inner mebrane c. Middle menbrane d. None.
34. Colorful organelles in plant cells are called:
a. Chloroplast b. Plastid c. Chromoplast d. Leucoplast.
35. Green chromoplast of a plant cell is…
a. Chloroplast b. Plastid c. Chromoplast d. Leucoplast.
36. Leucoplast is a storing organelle for
a. Protein b. Fats c. Starch d. All
37. ………… is a membranous layer present in the chloroplast.
38. Storage sac in plant and animal cell is…
a. Chloroplast b. Plastid c. Vacuole d. Mitochondria
39. Vacuole in animals is small while in a plant it is…
a. Absent b. Negligible c. Big d. None.
40. The function of the vacuole in plants is…
a. Digestion b. Antibody production c. Provides rigidity and turgidity to plant d. None.
41. Two types of cell division are
42. Mitosis produces two identical cells, while meiosis produces ……… unidentical cells.
a.1 b.2 c.3 d.4
Next:
- The Fundamental Unit of Life In-text & exercise question solution.
- The Fundamental Unit of Life Activity Explanation.
- Natural Resources MCQ.
- Tissues Class 9 MCQ.
- Diversity in Living Organisms MCQ.
- Why Do We Fall Ill MCQ
The Fundamental Unit of Life MCQ – Objective Questions with answers
Ref: Class 9 Science chapter 5.
Qno 8 Answer is freely permiable
Yes..
Ooooooo. Wow. You are so interested in science
Ooooooo
Thanks for your help
What is mitosis and meiosis
NICE QUESTIONS AND HELPS A LOT FOR PREPARING FOR EXAMS DURING CORONA PERIOD.
Excellent idea of answers along with explanation .
Very very nice
Amazing
Very best and excellent study material and questions
Nice and good idea of showing the answer
If u have MCQ on all subjects pls send the link
All questions were useful for me to prepare for exam compared to other websites it is good and nice
Nice
Nice it has many questions so I can prepared for my exam well.
You have all subject mcqs if you have please sende the link.
Easy compared to other websites
And the method is good
Liked It!
Boht hard op op op
yaa you are right
easy but good……………..////////////////////////============
It is cool but not good
Hmm
Ysetrday it’s so easy if we rad
easy
Bhot hard
It is good to revise what we have learnt from the chapter
Excellent questions, really helpful
It is really nice
It’s too good to just check yourself that how much you know about chapter .
Ohh really it’s very good to study
Very helpful
it very helpful for exam and weekly test
This is a very useful for exam and a class test also
it is very nice for us ,,,
Thank you so much for helping us .may God bless you dear
it very helpful for exam and weekly test
Yes , it was very helpful to us , because it may be come in exams also
Thanks for this, it will help in exam
Awesome! It helped me a lot:) It’s very helpful for exams or tests.
Nothing Sir
Very helping to us
It will help in exam
I have done all for the oral test. thanks for the questions
Very help ful
Helpful to us
Very helpful
Hlo yash i am asmita i have also done july 15 , 2020
I have done
It’s amazing
Thank You
It’s amazing. I really wanted this type of MCQ test. Good work.
I am elated now. And the MCQ’s are so engrossing. I love it.
Once again Thank You
Very helpful
Please refresh the page if the answer do not load.
Please show answers continuously
Please show answers
Why answers are not coming in this but these questions are good
Can you keep more harder so that it helps in practice
good MCQ’S
Yes
It’s was really verryyyyyyyyyyy helpful and dam good.
It is very helpful …But try to provide more outside MCQs without answers ..so that we will be blessed with more knowledge
Very helpful
Good
It is very helpful for us thanks
Hi,
Studdy.in is best
wow nice its helpful but u should also keep quiz so that we can also sove and without ans
This one is wonderful
This one is best