Structural Organisation in Animals MCQ Chapter 7 Objective questions NCERT Class 11 Biology
1. In a unicellular organism, a single cell performs:
- a. Digestion.
- b. Respiration.
- c. Reproduction.
- d. All.
2. Following is/are an example of a simple organism.
- a. Hydra.
- b. Planaria.
- c. Protozoa.
- d. All.
3. The outer layer of our skin consists of which tissue?
- a. Epithelial tissue.
- b. Connective tissue.
- c. Muscular tissue.
- d. Nervous tissue.
4. The largest organ in the human body is:
- a. Skin.
- b. Liver.
- c. Stomach.
- d. Heart.
5. The lining of a body cavity, duct, or tube comprises:
- a. Simple epithelial cells.
- b. Compound epithelial cells.
- c. Adipose cells.
- d. None.
6. Simple epithelium tissue consists of:
- a. Single-layer of cells.
- b. Only a double layer of cells.
- c. Triple-layer of cells.
- d. None.
7. Wall linings of blood vessels and air sacs of lungs are made of which epithelial cells?
- a. Squamous epithelium.
- b. Cuboidal epithelium cells.
- c. Columnar epithelium cells
- d. None.
8. Which type of ciliated epithelial cells makes the lining of the intestine?
- a. Squamous epithelium.
- b. Cuboidal epithelium cells.
- c. Columnar epithelium cells.
- d. None.
9. Goblet cells of the alimentary canal that secrete mucus is a _ _ _ _ _ Glandular epithelium.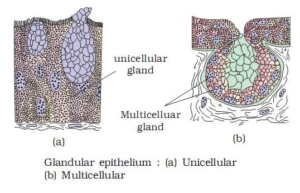

- a. Unicellular cuboidal.
- b. Unicellular columnar.
- c. Multicellular cuboidal.
- d. Multicellular columnar.
10. A salivary gland that secretes saliva is a _ _ _ _ _ Glandular epithelium.
- a. Unicellular cuboidal.
- b. Unicellular columnar.
- c. Multicellular cuboidal.
- d. Multicellular columnar.
11. Exocrine glands secretions are:
- a. Ductless hormones.
- b. Ductous enzymes.
- c. Ductless enzymes.
- d. Ductous hormones.
12. Endocrine glands secretions are:
- a. Ductless hormones.
- b. Ductous enzymes.
- c. Ductless enzymes.
- d. Ductous hormones.
13. Compound epithelium tissue consists of:
- a. Single-layer of cells.
- b. Only a double layer of cells.
- c. Only triple-layer of cells.
- d. More than one layer of cells.
14. Compound epithelial cells lines and give protection to:
- a. Skin.
- b. Buccal cavity.
- c. Pharynx.
- d. All.
15. Which of the following is an intercellular junction present in between two epithelial cells?
- a. Tight junctions.
- b. Adhering junctions.
- c. Gap junctions.
- d. All three.
Structural Organisation in Animals MCQ Chapter 7 Objective questions NCERT Class 11 Biology
16. The function of “tight junction” is to:
- a. Prevent leaking intercellular fluid.
- b. Keep adjoining cells together by cementing them.
- c. Provide communication by transferring ions and cytoplasm from nearby cells.
- d. All of the above.
17. The function of “adhering junction” is to:
- a. Prevent leaking intercellular fluid.
- b. Keep adjoining cells together by cementing them.
- c. Provide communication by transferring ions and cytoplasm from nearby cells.
- d. All of the above.
18. The function of “gap junction” is to:
- a. Prevent leaking intercellular fluid.
- b. Keep adjoining cells together by cementing them.
- c. Provide communication by transferring ions and cytoplasm from nearby cells.
- d. All of the above.
19. Which of the following is an example of connective tissue?
- a. Cartilage.
- b. Bones.
- c. Blood.
- d. All.
20. Connective tissue with no fibers is:
- a. Areolar tissue.
- b. Adipose tissue.
- c. Blood.
- d. Bones.
21. Specialised connective tissue which stores fat is:
- a. Areolar tissue.
- b. Adipose tissue.
- c. Blood.
- d. Bones.
22. Fluid connective tissue among these is:
- a. Areolar tissue.
- b. Adipose tissue.
- c. Blood.
- d. Bones.
23. Which type of muscular tissue is voluntary in action (responsible for Movement and locomotion):
- a. Skeletal.
- b. Smooth.
- c. Cardiac.
- d. All three.
24. Strongest muscles in a human body is at:
- a. Jaws.
- b. Wrist.
- c. Shoulder.
- d. Hip.
25. Muscles in internal organs like blood vessels, stomach, and intestine consist of which tissue?
- a. Skeletal.
- b. Smooth.
- c. Cardiac.
- d. All three.
26. Cardiac muscles in the heart contract and relaxes at the same time due to:
- a. Tight junctions.
- b. Adhering junctions.
- c. Gap junctions as intercalated discs.
- d. All three.
1. d. All. 2. d. All. 3. a. Epithelial tissue. 4. a. Skin. 5. a. Simple epithelial cells. 6. a. Single-layer of cells. 7. a. Squamous epithelium. 8. c. Columnar epithelium cells. 9. b.Unicellular columnar.10. d. Multicellular columnar. 11. b. Ductous enzymes. 12. a. Ductless hormones. 13. d. More than one layer of cells. 14. d. All. 15. d. All three. 16. a. Prevent leaking intercellular fluid. 17. b. Keep adjoining cells together by cementing them. 18. c. Provide communication by transferring ions and cytoplasm from nearby cells. 19. d. All. 20. c. Blood. 21. Adipose tissue. 22. c. Blood. 23. a. Skeletal. 24. d. Hip. 25. Smooth. 26. c. Gap junctions as intercalated discs.
Next:
- The Living world MCQ Biology Questions
- Biological Classification MCQ Questions with answers
- Plant Kingdom MCQ Biology Class Eleven
- Animal Kingdom MCQ Biology
- Morphology of Flowering Plants MCQ
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants MCQ Biology
- Structural Organisation in Animals MCQ
Structural Organisation in Animals MCQ Chapter 7 Objective questions NCERT Class 11 Biology
*****
Ref: Chapter 7, NCERT.
These questions are very easy. Plz make some level