Life Processes MCQ Class 10 chapter 6
Autotrophic Nutrition / Photosynthesis MCQ
1. Raw materials used in the autotrophic mode of nutrition is:
- A. Glucose, Starch, Fructose
- B. Protein, Fats
- C. Carbon dioxide, water
- D. Hydrogen, Oxygen
Which foods among these give us energy:
(i) Carbohydrates & fats
(ii) Proteins & mineral salts
(iii) Vitamins & minerals
(iv) Water & roughage
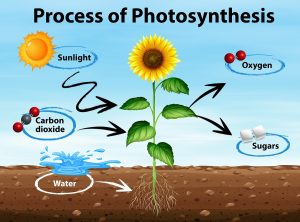

- A. Trapping energy of sunlight to form glucose.
- B. Synthesis of photosensitive compounds.
- C. Oxidation of glucose
- D. Oxidation of carbon dioxide
The green pigment used in photosynthesis is
- A. Phytochrome
- B. Chlorophyll
- C. Hemoglobin
- D. None
Chlorophyll is mainly located in which part of the plant
- A. Green leaf
- B. Bark
- C. Stem
- D. Root
Chlorophyll has a porphyrin ring with _ _ _ _ _ at the center.
- A. Iron (Fe)
- B. Chromium (Cr)
- C. Magnesium (Mg)
- D. Carbon (C)
Chlorophyll pigment is located in which organelle of a cell?
- A. Mitochondria
- B. Vacuole
- C. Plastid
- D. Chloroplast
Apart from the plant which microorganisms also do photosynthesis:
- A. Algae and cyanobacteria
- B. Fungi
- C. Paramecium
- D. Amoeba
Iodine solution turns a potato into blue-black in color. This indicates that potato contains:
- A. Fats
- B. proteins
- C. Starch
- D. Glucose
Table of Contents
Heterotrophic Nutrition MCQ
Mode of nutrition where an organism derives its food from the body of another living organism without killing it:
- A. Saprotrophic nutrition
- B. Parasitic nutrition
- C. Holozoic nutrition
- D. Autotrophic nutrition
Heterotrophic nutrition is
- A. The utilization of energy obtained by the plants.
- B. Breakdown of Glucose into energy
- C. Oxidation of Glucose
- D. All
Phagocytosis by amoeba is:
- A. Parasitic nutrition
- B. Holozoic nutrition
- C. Autotrophic nutrition
- D. Saprotrophic nutrition
Digestion of food in amoeba occurs in
- A. Nucleus
- B. Cytoplasm
- C. Food vacuole
- D. None
Human Digestive System MCQ
Saliva contains an enzyme that degrades starch into simple sugar. The enzyme is:
- A. Salivary Amylase
- B. Pepsin
- C. Trypsin
- D. None
What saliva does?
(i) Breaks down the complex starch into sugars. (ii) Breaks protein into amino acids. (iii) Absorption of vitamins. (iv) Break down of fats into fatty acids & glycerol.
The stomach produces acidic hydrochloric acid. Why
- A. Starch is broken down into simple glucose by it.
- B. To neutralize bases present in food.
- C. Pepsin needs an acidic medium to work upon proteins.
- D. None
Hydrochloric acid is secreted by
- A. Pancreas
- B. Small intestine
- C. Liver
- D. Gastric glands of the stomach
The difference between pepsin and trypsin is
- A. They work on different types of proteins
- B. They are secreted by different parts of the body viz. stomach, Pancrease respectively
- C. Trypsin do not need an acidic environment unlike pepsin
- D. All of the above
Bile juice is secreted by
- A. Stomach
- B. Saliva
- C. Liver
- D. None
The role of bile juice is
- A. Digestion of fat
- B. Emulsification of fat
- C. Digestion of starch
- D. None
An enzyme that degrades fats and oils into simpler fatty acid
- A. Lipase
- B. Cellulase
- C. Amylase
- D. Trypsin
Herbivores have a longer small intestines than a carnivore.
- A. True
- B. False
Absorption of most nutritional substances takes place in:
A. Stomach
B. Small intestine
C. Large intestine
D. Oesophagus
The small intestine is coiled to increase the surface area. What benefit does it get from the high surface area?
- A. Microorganism gets killed due to longer passage.
- B. Increases the rate of absorption of food
- C. Both are true
- D. None
Cellulase enzyme in ruminant and termites breaks
- A. Cellulose
- B. Starch
- C. Glucose
- D. Protein
The function of large intestine is mainly
A. Absorption of water
B. Assimilation of food
C. Digestion of fats
D. Digestion of carbohydrates
Respiratory System MCQ
A pair of an organ meant for respiration is…
a. Heart b. Kidney c. Lung d. Stomach.
Trachea/windpipe contains ‘c’ shaped cartilaginous ring. The function of this ring is to…
a. Trap pathogen b. Prevent the collapse of trachea c. Trap Dust and mites d. None
Alveoli are made of … tissue.
a. Connective tissue b. Fibrous tissue c. Muscular d. Epithelial (squamous) tissue.
Part of the mouth which prevents the entry of food into the trachea while swallowing is…
a. Epiglottis b. Tongue c. Pharynx d. Larynx.
The voice box is…
a. Epiglottis b. Tongue c. Pharynx d. Larynx.
Pharynx opens into the esophagus while larynx opens into …
a. Trachea b. Nasal passage c. Blood Vessels d. None.
Blood vessels that supply alveoli are…
a. Pulmonary Artery b. Pulmonary vein c. Carotid artery d. Jugular vein.
The functional unit of a lung is…
a. Trachea b. Bronchus c. Bronchiole d. Alveolus.
Transportation MCQ
A human heart is situated in a cavity slightly right to the sternum. This cavity or notch is…
a. Pulmonary cavity b. Cardiac notch c. Buccal cavity d. None.
The human heart has four chambers. Two atria and two ____.
a. Ventricles b. Septum c. Vena cava d. None.
The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood while the left atrium receives…
a. Air b. Water c. Oxygenated blood d. Lymphatic fluid.
Cardiac tissue is an example of which type of tissue?
a. Muscular b. Nervous c. Glandular d. Connective.
How many times the human heartbeats in a minute?
a. 60 b. 72 c. 120 d. 108.
The duration of one complete cycle of heart is…
a. 0.8(60/72) b. 1.0(60/60) c. 0.6(60/96) d. None.
The strongest chamber of the human heart is…
a. Lt. Atrium b. Lt. Ventricle c. Rt. Atrium d. Rt. ventricle.
The pressure inside a blood vessel in mm of Hg is:
a. 120/80 b. 180/120 c. 80/120 d. 120/90.
Arteries carry oxygenated blood. The only artery that carries deoxygenated blood is…
a. Carotid artery b. Pulmonary Artery c. Renal artery d. none.
Excretion MCQ
The major excretory organ is…
a. a pair of kidneys b. a pair of lungs c. Spleen d. Liver.
The functional unit of a kidney is…
a. Glomerulus b. Nephron c. PCT d. DCT.
The number of nephrons (in million/10 lakh) in each kidney is…
a. 1 million b. 2-3 Million c. 5 million c. 10 million.
Do we find glucose in urine normally?
a. Always b. Never c. Only in case renal impairment d. Sometimes depending on intake.
The contraction & expansion movement of the walls of the intestine is called:
(i) translocation (ii) transpiration (iii) peristaltic movement (iv) digestion
Egestion is regulated by
(i) liver (ii) anus (iii) small intestine (iv) anal sphincter
See also: Life Processes Objective Questions.
For the detailed answer, see explained: Notes and questions on Life Processes.
Life Processes MCQ Miscellaneous questions
-
Fungi have:
(i) Parasitic nutrition
(ii) Holozoic nutrition
(iii) Autotrophic nutrition
(iv) Saprotrophic nutrition
-
Roots of a plant absorb water from the soil through :
(i) diffusion
(ii) transpiration
(iii) osmosis
(iv) None of these
-
In plants Respiratory exchange of gases takes place through:
(i) Lenticels
(ii) Vacuoles
(iii) Xylem
(iv) Stomata
-
water & minerals conducting tissue in the plant is:
(i) Xylem
(ii) Phloem
(iii) Parenchyma
(iv) Collenchyma
-
Food tranporat through phloem tissue is called:
(i) transpiration
(ii) translocation
(iii) respiration
(iv) evaporation
-
Permeable tissue which transport nutrition and oxygen to nearby cells is:
(i) artery
(ii) capillary
(iii) Vein
(iv) Haemoglobin
-
Apart from blood there is another fluid which also circulate in our body. The fluid is:
(i) Platelets
(ii) RBC
(iii) Lymph
(iv) Plasma
-
Single circulation is found in _ _ _ _ _ :
(i) hyla, Rana, Draco
(ii) whale, dolphin, turtle
(iii) labeo, chameleon, salam&er
(iv) hippocampus, exocoetus, anabas
-
Name the tubethat connects the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
(i) Urethra
(ii) Nephron
(iii) Tubule
(iv) Ureter
- In kidneys Selective reabsorption of glucose, amino acids, minerals & water into the blood takes place in:(i) Tubule
(ii) Glomerulus
(iii) Bowman’s capsule
(iv) Ureter
-
Oxygenation of impure blood occurs in:
(i) Heart
(ii) Lungs
(iii) Ureter
(iv) Kidneys
-
artificial removal of urea from blood is termed:
(i) osmosis
(ii) filtration
(iii) dialysis
(iv) double circulation
-
Passage of urine occur through:
(i) Kidney → urinary bladder → urethra → ureter
(ii) Urinary bladder → ureter → kidney → urethra
(iii) Kidney → ureter → urethra → urinary bladder
(iv) Kidney → ureter → urinary bladder → urethra
A gland not related to digestion is
(i) liver
(ii) salivary glands
(iii) pancreas
(iv) adrenal
-
Major place for protein digestion is
(i) Stomach
(ii) Small intestine
(iii) Large intestine
(iv) None
-
-
Which of the following part of the Digestive system do not carry digestion:
(i) ileum
(ii) stomach
(iii) mouth
(iv) esophagus
-
-
-
Yeast breaks glucose into:
(i) alcohol, CO2 & 36 ATP
(ii) CO2, H20 & 36 ATP
(iii) alcohol, CO2 & 2ATP
(iv) lactic acid, CO7 & 2 ATP
-
-
-
A large quantity of one is removed from our body by lungs:
(i) CO2 & H20
(ii) CO2 only
(iii) CO only
(iv) ammonia
-
-
-
In respiration, air passes through
(i) Pharynx → nasal cavity → larynx → trachea bronchi → bronchioles
(ii) Nasal cavity → pharynx → larynx → trachea → bronchi → bronchioles
(iii) Larynx → nasal cavity’ → pharynx → trachea
(iv) Larynx → pharynx trachea → lungs
-
-
-
A biochemical molecule of blood that combines with oxygen & helps in its transportation is
(i) water
(ii) urea
(iii) haemoglobin
(iv) acetylcholine
-
-
-
Loss of water in the form of water vapor through stomata is called
(i) transportation
(ii) transpiration
(iii) guttation
(iv) translocation
-
-
-
The closed circulatory system of humans is:
(i) One-way channel.
(ii) Double Cyclic channel.
(iii) Two-way channel.
(iv) None.
-
-
-
Normal blood pressure (systolic/diastolic) is
(i) 120/80 mm of Hg
(ii) 160/80 mm of Hg
(iii) 120/60 mm of Hg
(iv) 180/80 mm of Hg
-
-
-
An instrument that measures blood pressure is:
(i) barometer
(ii) sphygmomanometer
(iii) photometer
(iv) manometer
-
-
-
Identify the false statement:
(i) The right atrium of the heart receives oxygenated blood from the body.
(ii) The excretion in flatworms occurs through flame cells.
(iii) A human kidney contains 1 million nephrons.
(iv) Tracheids are nonliving conducting tissues.
-
-
- Liver secretes bile through the bile duct into:
(i) Stomach
(ii) Small intestine
(iii) Large intestine
(iv) Oesophagus
- Liver secretes bile through the bile duct into:
-
-
The Air turns lime water milky because lime reacts with _ _ _ _ (gas present in the air)
(i) oxygen
(ii) carbon dioxide
(iii) nitrogen
(iv) water vapor
-
-
-
Structural and functional unit of kidneys is:
(i) ureter
(ii) urethra
(iii) neurons
(iv) nephrons
-
-
-
Oxygen evolved during photosynthesis in a plant cell comes from
(i) water
(ii) chlorophyll
(iii) carbon dioxide
(iv) glucose
-
-
-
The opening & closing of the stomatal pore depends upon
(i) oxygen
(ii) temperature
(iii) Turgor pressure in the guard cell.
(iv) the concentration of CO2 in stomata
-
Check out other MCQs also:
- Our Environment MCQ
- Sources of Energy MCQ
- Heredity and Evolution MCQ
- Chemical reactions and equations MCQ
- Life Processes MCQ
- Life Processes objective questions
- Control and Coordination MCQ
- How Do Organisms Reproduce MCQ
Life Processes MCQ Class 10 chapter 6
Ref: NCERT.
It’s wonderful …. tomorrow my exam of science so I prepare MCQs questions ..it’s very helpful seriously .. thanks a lot
Thanks a lot for helping us in exam thanks
Plssss
Can you give sst . Hindi.English .Maths
corrected
In the first question it is written that kidney is made up of 1 million of nephron and in another question … It is considered a false statement .. why ??
The carbon dioxide we exhale contains a very small amount of water…..Thus both CO2 and H2O are considered
Thanks for letting me know. Now the answer is corrected.
A large quantity of one is removed from our body by lungs:
Isnt the answer wrong..? I guess its CO2 only.. how will we exhale H2O?
Good for preproduction
But so long
Wow!
Renal artery
1. Carrie’s oxygenated blood from heart to kidney
2. Blood flow with jerk.
3. Blood flows under pressure.
4. Valves are absent.
5. They are deep seated.
Renal vein
1. Carrie’s blood from kidneys to heart.
2. Flows smoothly.
3. There is little pressure.
4. Valves are present.
5. It is superficial
Wow ! Thats really Great ! But I want to DOWNLOAD pdf of this ‽
Can You plz send ?
RENAL ARTERY:
1. It gives the impure blood to the kidney.
2. Amount of urea in blood is high in renal artery.
RENAL VEINS:
1. It takes away the pure blood away from the kidney.
2. Amount of urea in blood is low.
I know only 2 points also I am not sure about rest 3 points.
What is the difference between renal artery and renal vein 5 point
Plz send some important questions pdf
Please