Science Class 6 Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances Summary/revision notes
We can measure distances in various ways like by hands, handspan, foot, etc. These measurements are not precise and vary from person to person. So we use a standard convention which is accepted by everyone. It the Internation system of the unit (SI).
As per SI
1 meter equals to 100 centimeter or 1000 milimeter.
For larger distance we use kilometre.
One kilometre equals to 1000 meter.
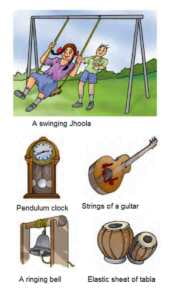
Table of Contents
Motion and its type:
An object is said to be in motion if its place varies from time to time. On the basis of the movement a motion can be:
Rectilinear: Movement on a straight path.
Circular: Movement on a circular path. e.g. a moving fan.
Periodic motion: In this motion, an object repeats its place after some time. For example, movement of a swinging jhoola, pendulum, strings of guitar etc. are examples of periodic motion.
Combination of circular motion and rectilinear motion: In this type of motion object shows a circular motion as well a rectilinear motion. For example a rolling ball, a moving cycle wheel.
See also:
Exercise solution NCERT class 6 Chapter 10.