- Which of the following is a plant hormone?
Ans: Cytokinin
2. The gap between two neurons is called a
Ans: Synapse
3. The brain is responsible for
Ans: All of these (Thinking, regulating the heartbeat, balancing the body)
4. What is the function of receptors in the body? Think of situations where receptors do not work properly. What problem are likely to arise?
Ans: During the whole life span an organism including us, interact with the surrounding.
With eyes, we see things. By touch, we know whether the object is cold or hot, hard or soft. Our taste buds in the tongue tells us about the flavour of the food. With nose we detect the smell, with ear we listen to the sound.
All of these are receptors which send specific information about the surrounding to our brain.
Our brain analyses the information and we do things which are good for us.
Living life will become difficult if any of these functions are stopped.
For example, if our eyes stop working, we will not be able to see the surrounding. Walking travelling will become difficult.
If our taste buds of tongue loose sensation we will not feel any taste in food, every food will feel alike, and we will not be able to judge good food and bad food.
5. Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its function.
Ans:
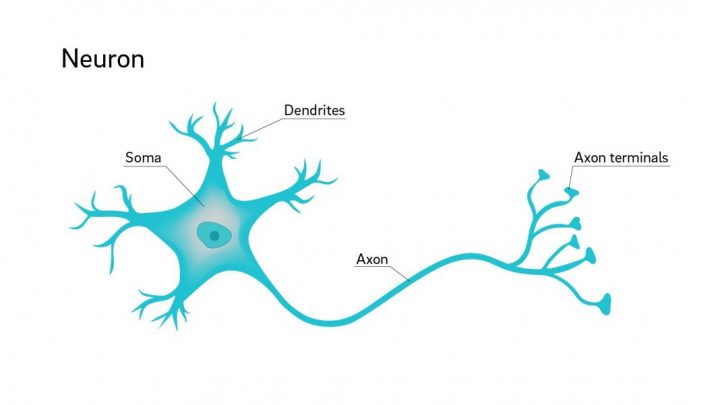
A neuron is the structural and functional unit of our nervous system. It consists of axons, Cell body – Soma, and dendrites.
Axon terminal receives the signal from the environment like touch, pressure, heat, cold, taste etc. and transmit it to dendrite.
Dendrite receives the signal and spread the information to the nearby axon.
6. How does phototropism occur in plants?
Plant show movent towards the light. We call this phenomenon as Phototropism.
- +ve Phototropism: Shoot
- -ve Phototropism: Root
Plant shoot exposed to light release auxin hormone. This hormone diffuse to unexposed part of the plant. Here it induces cell growth. As a result plant shoot bend towards the light.
High concentration of auxin in root show inhibitory action. It reduces the growth of the root in the unexposed part of the root. As a result, root bend away from the light.
For more details check Explained Activity 7.2.
7. Which signal will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
Ans: Vertebrae bones around the spinal cord protect very well from injury. In most of the cases, only the bones are damaged. In some cases, the spinal cord is intact but loses its function.
The spinal cord is the major centre for reflex action and limb movement. In case it is damaged various sensation like heat, cold, touch, the pressure of hands and skin will stop. Since spinal cord also controls the movement of limbs, we will also not able to move our hands or feet.
Cranial nerves control smell, visual and auditory receptors. So there will not be any effect on them.
8. How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
Ans: Chemical coordination in plant occur by some chemical. We call them plant hormone or Phytohormone.
They are:
Auxin: Cell elongation, root development
Gibberellin: Shoot developement.
Cytokinin: Promote cell division
Abscisic acid: Older leaves produce abscisic acid. It helps in migration of useful component like chloroplast into new leaves.
Ethylene oxide: Ripening of fruit.