Anatomy of Flowering Plant MCQ Biology Class 11 Chapter 6 NCERT
1. Anatomy is the study of:
- a. Internal parts.
- b. External parts.
- c. Morphological parts.
- d. None.
2. Which among these are types of plant tissues are?
- a. Meristematic
- b. Permanent tissue.
- c. Both
- d. None.
3. Apical and intercalary meristem are:
- a. Primary meristem.
- b. Secondary meristem.
- c. Tertiary meristem.
- d. None.
4. Following is a matured tissue:
- a. Meristematic.
- b. Permannet tissue.
- c. Both.
- d. None.
5. Permanent tissue with all cells simar in structure and function is:
- a. Simple permanent tissue.
- b. Complex permanent tissue.
- c. Meristematic tissue.
- d. None.
6. Following are the examples of simple permanent tissue:
- a. Parenchyma.
- b. Collenchyma.
- c. Sclerenchyma.
- d. All of the above.
7. Which tissue among these can photosynthesize or have storage or secretory function?
- a. Parenchyma.
- b. Collenchyma.
- c. Sclerenchyma.
- d. None.
8. Which tissue among these is dead tissue?
- a. Parenchyma.
- b. Collenchyma.
- c. Sclerenchyma.
- d. None.
9. Example of complex tissues is/are:
- a. Xylem.
- b. Phloem.
- c. Both.
- d. None.
10. Conducting tissue for water and mineral is:
- a. Xylem.
- b. Phloem.
- c. Both.
- d. None.
11. Plant transport food through:
- a. Xylem.
- b. Phloem.
- c. Both.
- d. None.
12. Following may be a part of xylem tissue:
- a. Tracheids.
- b. Vessel.
- c. Xylem parenchyma.
- d. Xylem fibers.
- e. All.
13. The xylem which forms first and later respectively is:
- a. Protoxylem, metaxylem.
- b. Metaxylem, protoxylem.
- c. Xylem parenchyma.
- d. None.
14. Arrangemnet of xylems in stems is:
- a. Exarch
- b. Mesarch
- c. Endarch.
- d. None.
15. Arrangemnet of xylems in stems is:
- a. Exarch
- b. Mesarch
- c. Endarch.
- d. None.
16. Which part of the plant tissue system contain stoma and guard cells?
- a. Epidermis
- b. Cuticle.
- c. Pith.
- d. None.
17. Stoma closes when turgour pressure in guard cell:
- a. Increase.
- b. Decrease.
- c. Closure of stoma does not depend on turgor pressure.
- d. None.
18. Ground tissue include all except:
- a. Epidermis.
- b. Vascular tissue.
- c. Both.
- d. None.
19. Ground tissue of leaves that contain chlorophyll containing cells in the plant is:
- a. Cuticle.
- b. Epidermis.
- c. Mesophyll.
- d. Endodermis.
20. Open vascular bundle is present in:
- a. Dicot stem.
- b. Dicot root.
- c. Monocot stem.
- d. None.
Anatomy of Flowering Plant MCQ Biology Class 11 Chapter 6 NCERT
21. In radial vascular bundle, VB alternates at different: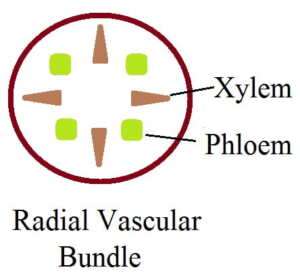

- a. Diameter
- b. Periphery
- c. Radii
- d. Centre.
22. In conjoint vascular bundle xylem an phloem are:
- a. Joint.
- b. At the same radii.
- c. At different radii.
- d. Both a and b.
23. Radial vascular bundle is present in:
- a. Root.
- b. Stem.
- c. Leaves.
- d. Both b and c.
24. Conjoint vascular bundle is present in:
- a. Root.
- b. Stem.
- c. Leaves.
- d. Both b and c.
25. Casparian strips are water impermeable walls. It is found in the outer layer of:
- a. Epidermis.
- b. Cortex.
- c. Endodermis.
- d. Pith.
26. _ _ _ _ _ is the parenchymatous tissue present between the xylem and the phloem.
- a. Connective tissue.
- b. Conductive tissue.
- c. Conjunctive tissue.
- d. None.
27. Pith is large and developed in:
- a. Monocot root.
- b. Monocot stem.
- c. Dicot root.
- d. None.
28. Ring arrangement is a characteristic of :
- a. Monocot root.
- b. Monocot stem.
- c. Dicot root.
- d. Dicot stem.
29. Bulliform cells regulate:
- a. Water.
- b. Glucose.
- c. Minerals
- d. Sucrose.
30. Secondary growth is absent in:
- a. Monocot.
- b. Dicot.
- c. Both.
- d. None.
31. The formation of annual ring is due to _ _ _ _ _ _ variation in the activty of cambium.
- a. Temperature.
- b. Seasonal.
- c. Rainfall.
- d. Altitude.
32. Folowing part of plant conduct water and mineral.
- a. Heartwood.
- b. Sapwood.
- c. Both.
- d. None.
Read also:
Structural Organisation in Animals MCQ.
Morphology of Flowering plants MCQ.
Biological Classification MCQ.
See other chapters MCQ: MCQ Biology class 11.
Answer
1. a. Internal parts. 2. a.Meristematic. 3. a. Primary meristem. 4. b. Permanent tissue. 5.a. Simple permanent tissue. 6.d. All of the above. 7. a. Parenchyma. 8.c. Sclerenchyma. 9.c. Both. 10. a. Xylem. 11. b. Phloem. 12. e. All. 13. a. Protoxylem, metaxylem. 14. a. Exarch. 15. c. Endarch. 16. a. Epidermis 17. b. Decrease. 18.c. Both. 19.c. Mesophyll. 20. a. Dicot stem. 21. c. Radii. 22. d. Both a and b. 23. a. root. 24. d. Both b and c. 25. c. Endodermis. 26. c. Conjunctive tissue. 27. Monocot root. 28. d. Dicot stem. 29. a. a. Water. 30. a. Monocot. 31. b. Seasonal. 32. b. Sapwood.
Anatomy of Flowering Plant MCQ Biology Class 11 Chapter 6 NCERT
Ref: Chapter 6, NCERT.