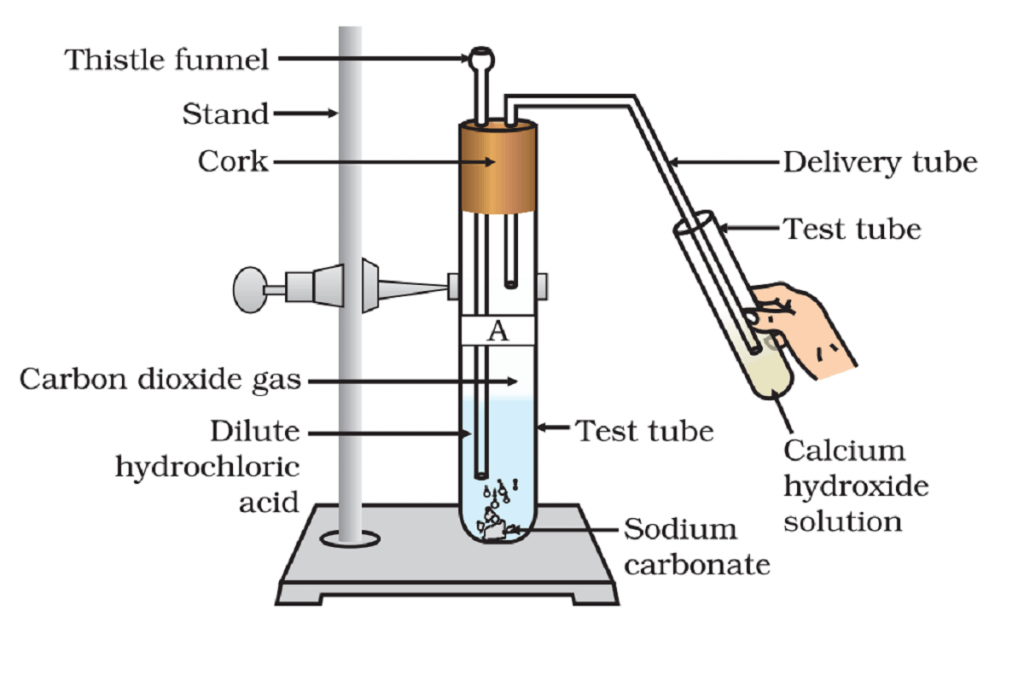
Activity 2.5 NCERT Class 10 Science, Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts.
Procedure:
Activity 2.5 asks us to react metal carbonates and metal hydrogen carbonate with acids and see if any gas evolves; check also if gas gives a precipitate with quick lime.
Observation:
When we add acid to carbonates and hydrogen carbonates of metal, bubbles start appearing from the carbonates. When we pass this air to a quick lime solution, it turns the lime water milky.
Explanation:
- Carbonates and hydrogen carbonates of metal contain carbonate group (CO3) in it. The metal forms its salt with acid and produces carbon dioxide gas and water.
Na2CO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) ——–> 2NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
NaHCO3(s) + HCl(aq) ——–> NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) ——–> CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
2. Carbon dioxide reacts with quick lime (CaO) and form slaked lime (Ca(OH)2). This is a slow process unless water is present in the lime. Carbon dioxide further reacts with slake lime and form calcium carbonate. The newly formed Calcium carbonate is insoluble in water. Its powder form makes water milky. This process is explained in Activity 1.4.
Ca(OH)2(aq) + CO2(g) ——–> CaCO3(s) + H2O(l)
Inference/conclusion:
This experiment shows that all metal carbonates and metal hydrogencarbonates react with acids and form carbon dioxide.
Next: How to use PH indicator to know the completion of a reaction, Activity 2.6
See also:
The reaction of zinc with a base. Activity 2.4.
I have added a few more points above. Please read again. Fore more check activity 1.4.
Sir we pass co2 gas through ca(OH)2 which is slaked lime note cao
My question is 2.5activity in science activty based question anwers